43 moss plant labelled diagram
Label The Structures On This Diagram Of A Moss - Diagram World Label the structures on this diagram of a moss. Drag the labels onto the diagram below. This growth form is due to their thin body parts and lack of vascular structures that would support upward growth. Not all labels will be used. Liverworts hornworts and mosses. Moss - Wikipedia Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta ( / braɪˈɒfətə /, [3] / ˌbraɪ.əˈfaɪtə /) sensu stricto. Bryophyta ( sensu lato, Schimp. 1879 [4]) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. [5] Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats ...
Draw a Labelled Diagram of Gametophyte of Moss - QS Study Draw a Labelled Diagram of Gametophyte of Moss. Gametophyte of moss: Gametophyte of moss plant is haploid (n). Its body is divided into two stages. Protonema: Spores produced from the moss capsule germinate in favorable conditions. Spores germinate to form a filamentous, branched and algae-like plant, called protonema.

Moss plant labelled diagram
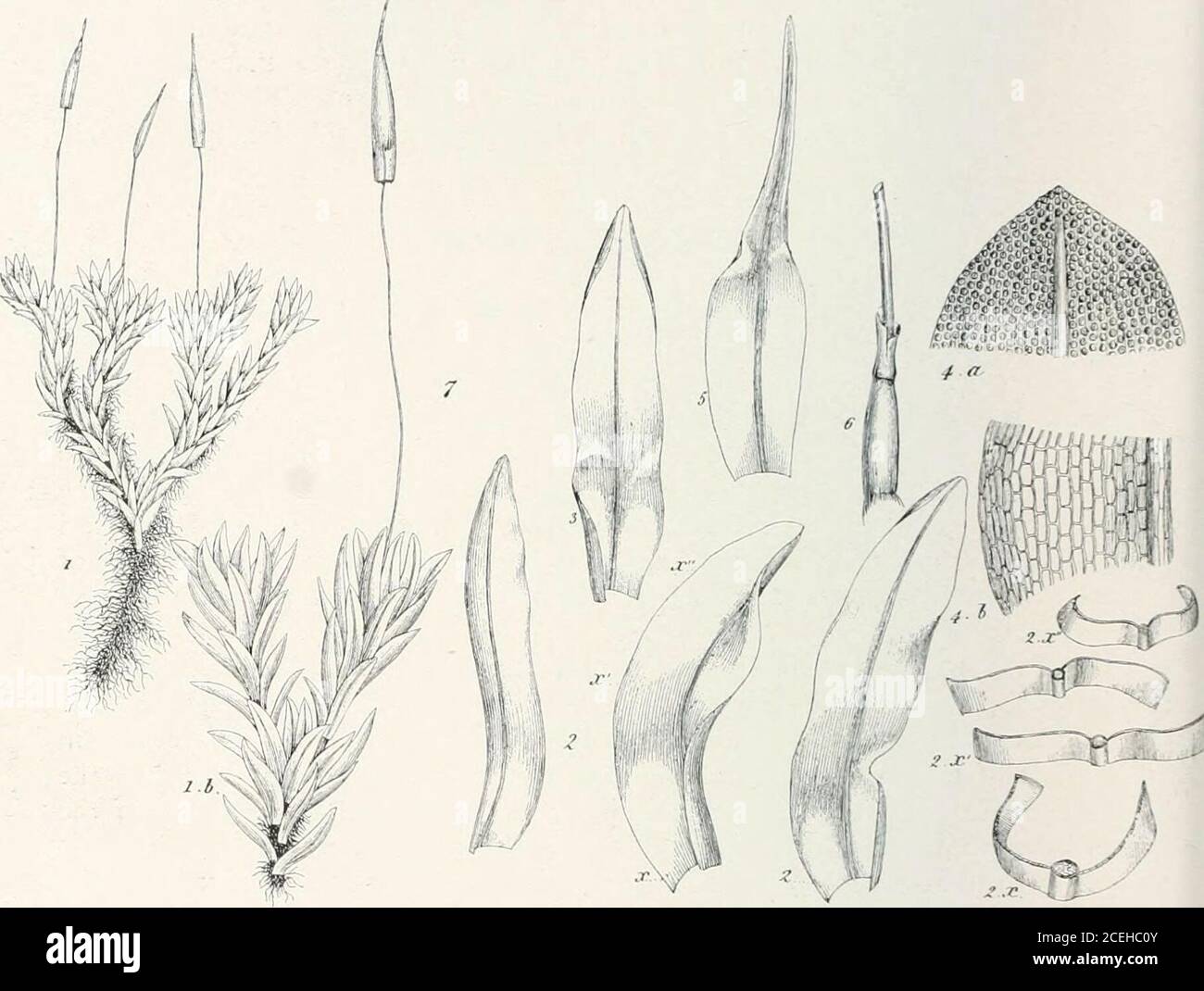
moss | Definition, Characteristics, Species, Types, & Facts Many small plants bearing the name moss are not in fact mosses. The "moss" found on the north side of trees is often the green alga Pleurococcus. Irish moss ( Chondrus crispus) is a red alga. Beard moss ( Usnea species), Iceland moss ( Cetraria islandica ), oak moss ( Evernia prunastri ), and reindeer moss ( Cladonia species) are lichens. PDF Morphology of Mosses (Phylum Bryophyta) - eFloras.org The fundamental moss leaf consists of a unistratose lamina and a multistratose costa or midrib (Fig. 3). However, in a few families, the entire leaf is multistratose, and in many others, leaf margins are multistratose, or otherwise differentiated from the rest of the lamina (Fig. 4). The Moss Life Cycle | Moss Gametophyte, Reproduction Parts & Diagram ... Moss life cycle diagram: the red boxes show the male antherdial part while the blue boxes show the female archegonial part, both are required for sexual reproduction. Both of the mature...
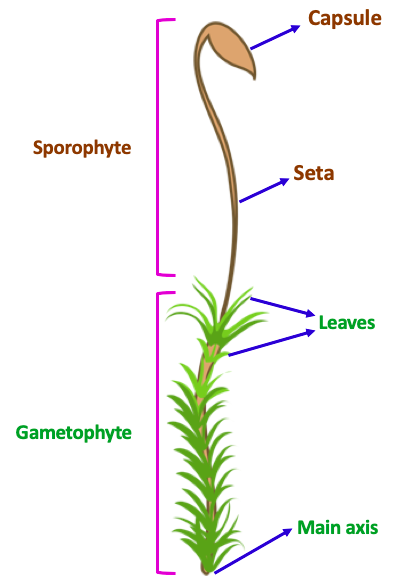
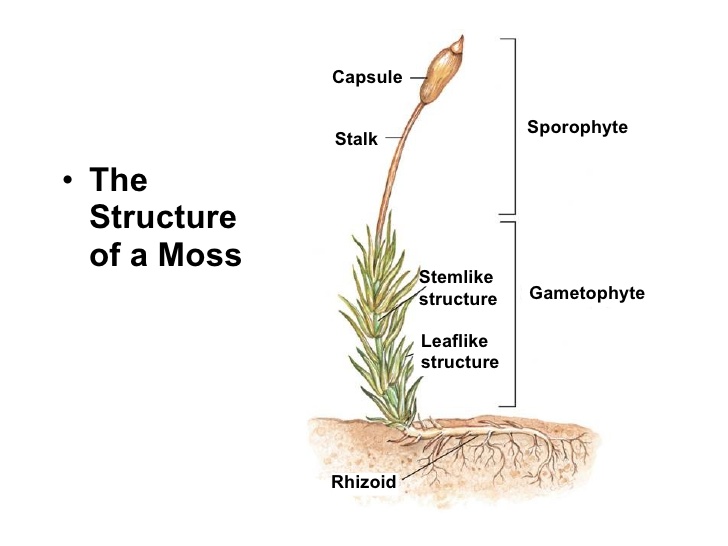
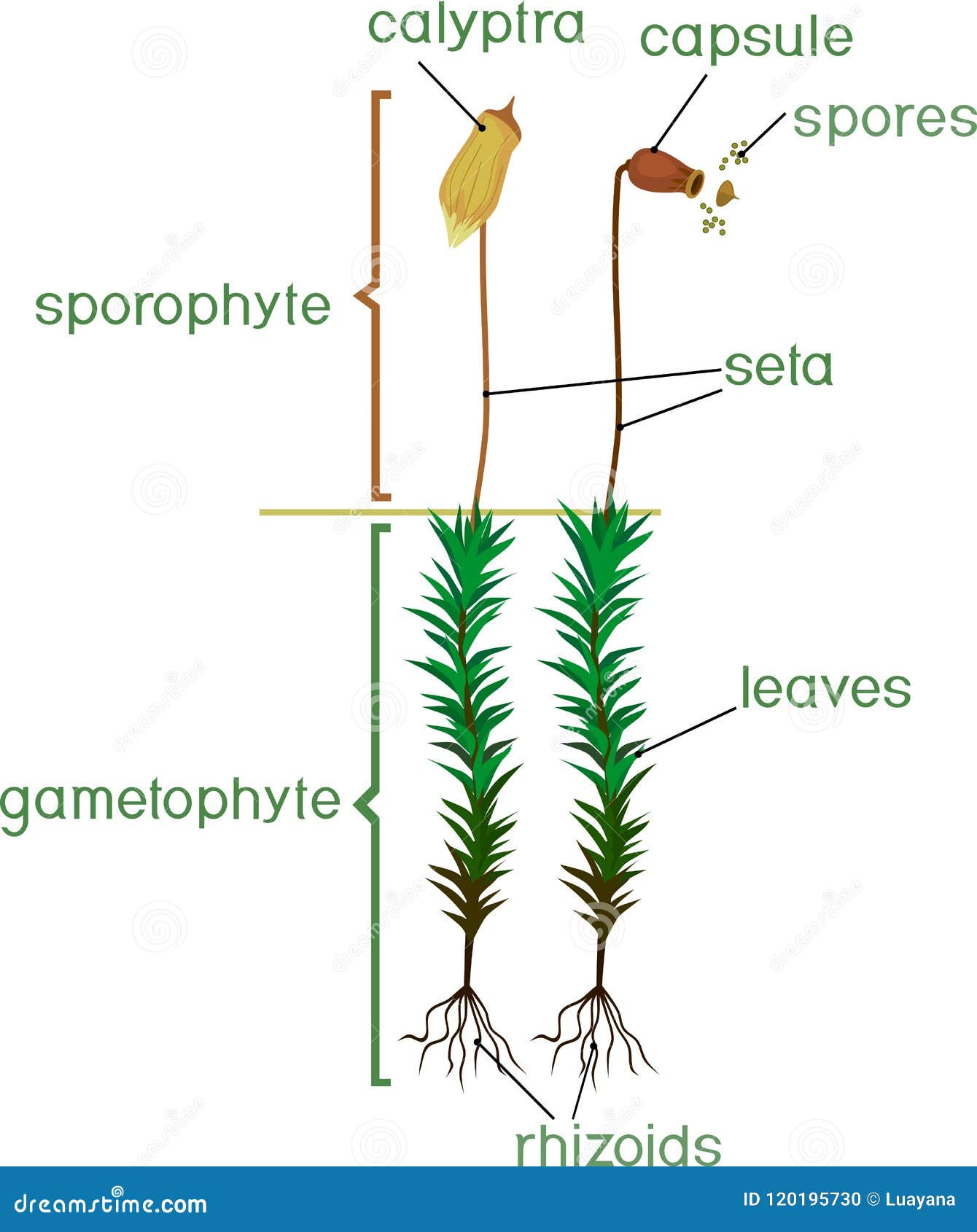
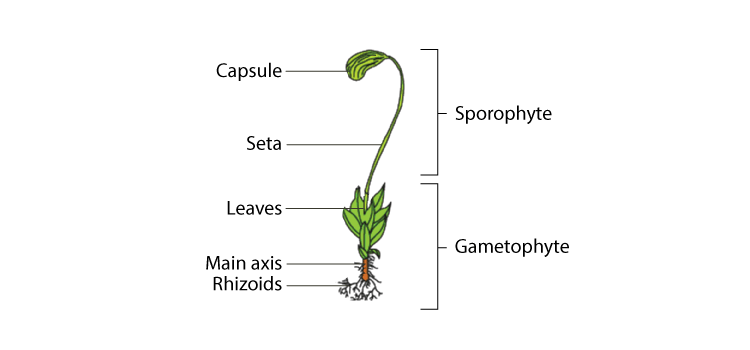
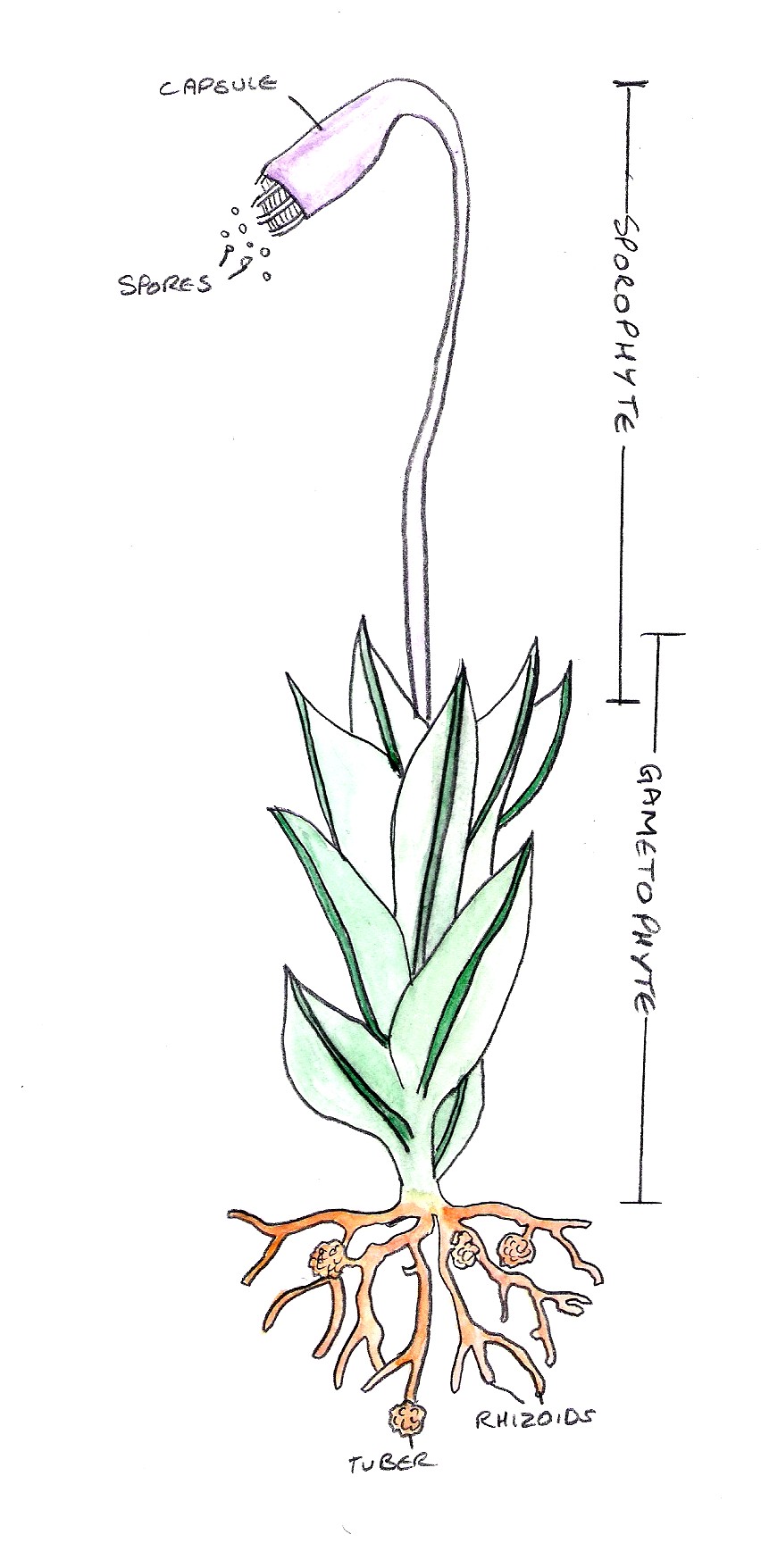
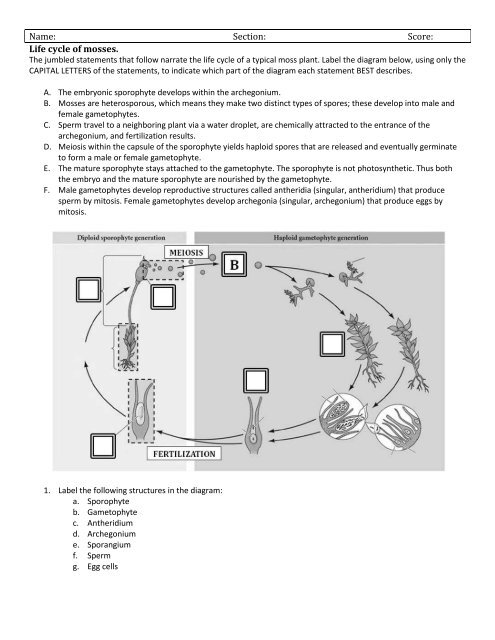
Moss plant labelled diagram. biology 252 plant morphology and systematics home page - Moss Plant ... Labeled Diagram Of The Moss Plant, Anatomy Of Plants, 14 Plant Kingdom Part Two, Antheridium Plant Anatomy Britannica, 4 (3179 votes) Download Wallpaper / Select Resolution Garden Guides | Parts of a Moss Plant Moss Structure Mosses lack true roots, but they do have grasping, rootlike structures called rhizoids. The aboveground parts can be delineated into two sections: the gametophyte and the sporophyte. The gametophyte is the base of the moss, with a stem and a soft cluster of leaves. labelled diagram of Sporophyte of Moss - QS Study labelled diagram of Sporophyte of Moss Fungus The sporophyte is the diploid phase of the alternation of generations, a method which allows sexual and asexual reproduction to prevent destructive genes to be reproduced. Moss is a non-vascular plant, meaning that it has no internal system to transport water. Solved Name: Life cycle of mosses. The jumbled statements - Chegg Question: Name: Life cycle of mosses. The jumbled statements that follow narrate the life cycle of a typical moss plant. Label the diagram below, using only the CAPITAL LETTERS of the statements, to indicate which part of the diagram each statement BEST describes. Section: Score: A. B. The embryonic sporophyte develops within the archegonium.
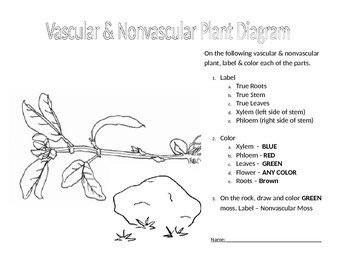
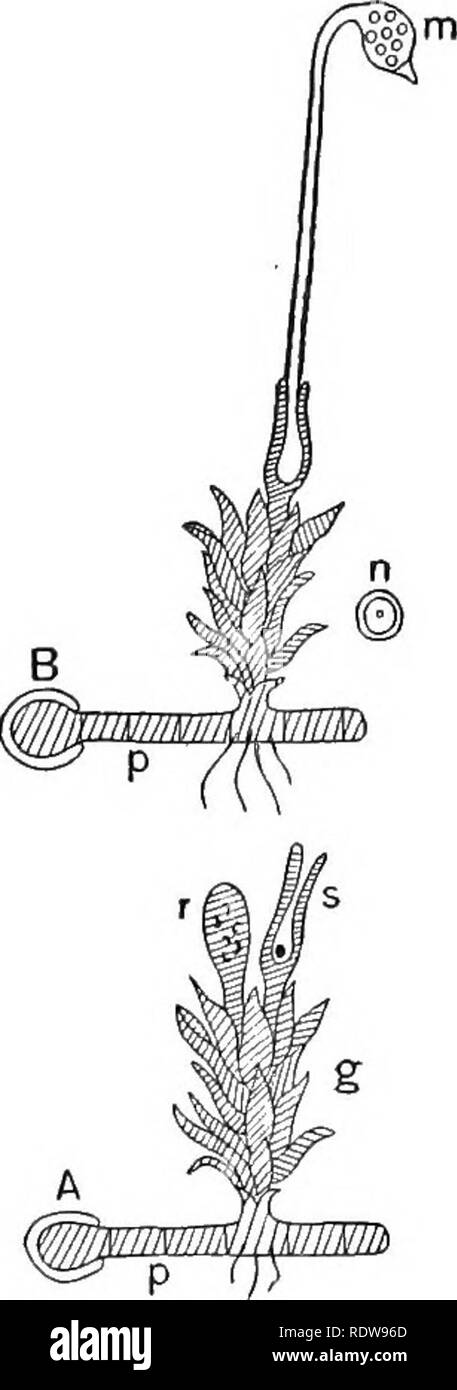
Mosses - Brian McCauley The slide labeled Mnium life history has multiple specimens on the same slide, showing different parts of the life history of this moss: young gametophyte, antheridial head and archegonial head (parts of male and female gametophytes), and capsule (part of the sporophyte). Make sure you see them all. Young gametophyte Life Cycle of a Moss - Infographic - STEM Lounge Each archegonium holds one egg, in a swollen section called the venter. The sperm enter the archegonium through the narrow channel in its neck. Fertilization occurs in the archegonium to form a diploid zygote. Once one archegonium in a group has been fertilized, in many cases the others lose the ability to be fertilized. Label Plants Diagram | Quizlet shines and gives energy. roots. take in water and nutrients. soil. contains water nutrients. stem. carries water and supports plant. leaf. uses energy from sunlight. What is Moss? | Characteristics, Facts, Examples, Structure ... As mentioned above, moss is a bryophyte. Bryophytes include mosses, hornworts, liverworts, and lichen, and though they look very different from other land plants, they still make their own food by...
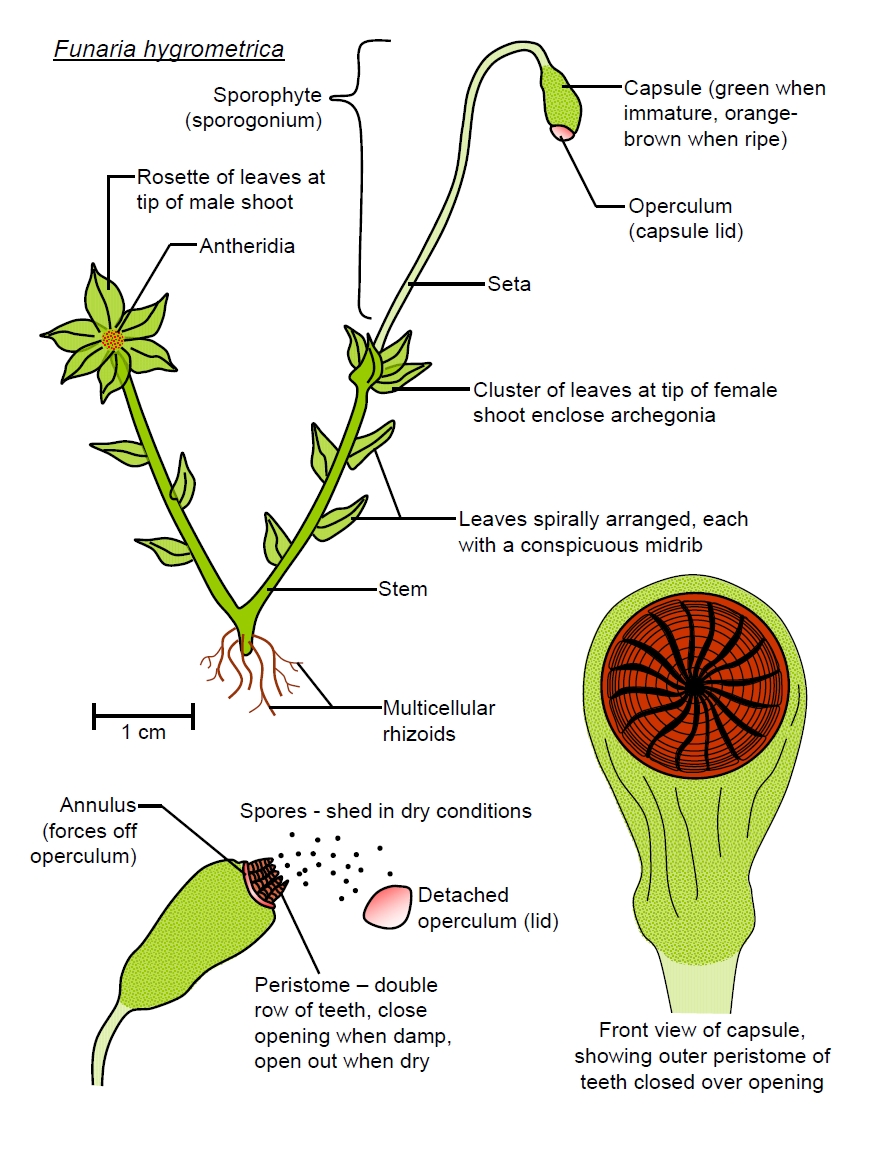
Moss Life Cycle - Andover In the common haircap moss, Polytrichum commune (shown here), there are three kinds of shoots: female, which develop archegonia at their tip; . A single egg forms in each archegonium.; male, which develop antheridia at their tip; . Multiple swimming sperm form in each antheridium.; sterile, which do not form sex organs. In early spring, raindrops splash sperm from male to female plants. The following image gives a basic diagram of a typical moss plant ... The following image gives a basic diagram of a typical moss plant. Label some of the important parts of the plant, and identify which structures represent the sporophyte and gametophyte phases. An illustration shows a moss plant. The leaf-like parts and rhizoids are labeled as C and D respectively. Together they are labeled as B. PDF Lab 12: Bryophytes : Mosses and Liverworts (and hornworts) Plant Biology, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL 62901-6509 Comparison of Moss and Liverwort Characteristics Leafy liverworts: Class Jungermanniidae • Gametophytes have leaves without costa (midvein) • Leaves inserted at angle to stem. • Leaves in 2-3 rows. • Sporophyte has a transluscent stalk, capsule black and egg-shaped Structure of a moss leaf - Mosses - Te Ara Most moss leaves are very simple and consist of a single layer of photosynthetic cells. Water and gases from outside pass easily into the cells. This moss, Distichophyllum kraussei, has elongated cells on its leaf margin and a central thickening, known as a nerve, that supports the leaf. Share this item.
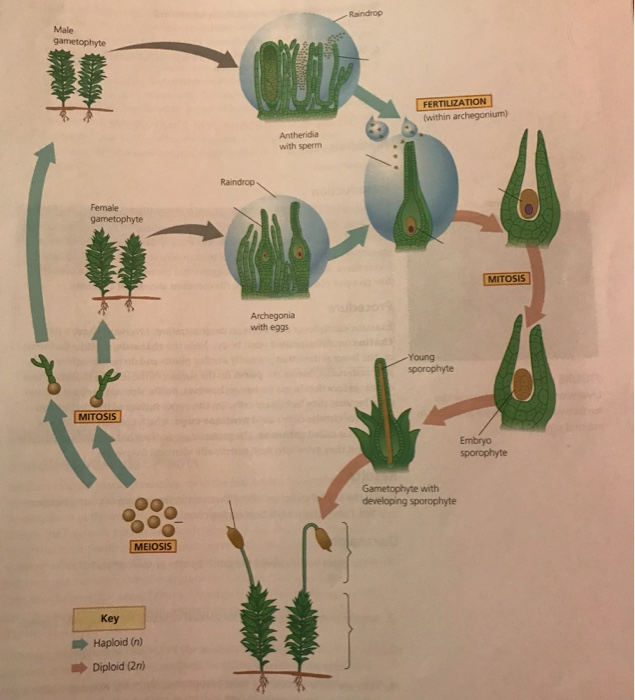
moss: life cycle - Students | Britannica Kids | Homework Help The life cycle of most mosses begins with the release of spores from a capsule, which opens when a small, lidlike structure, called the operculum, degenerates. A single spore germinates to form a branched, filamentous protonema, from which a leafy gametophyte develops. The gametophyte bears organs for sexual reproduction. Sperm, which are released by the mature antheridium (the male ...
Solved Label the structures on this diagram of a moss. Drag - Chegg Drag | Chegg.com. Science. Biology. Biology questions and answers. Label the structures on this diagram of a moss. Drag the labels onto the diagram below. Not all labels will be used. Question: Label the structures on this diagram of a moss. Drag the labels onto the diagram below.
Moss Diagram: Biology | Biology plants, Evolution of plants, Plant science Morphology of Flowering Plants Morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. The word "morphology" is from the Greek word, study, research. The biological concept of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the ...
PLANTS & GARDENING :: PLANTS :: MOSS :: STRUCTURE OF A MOSS image ... Rootlike filament enabling the moss to anchor itself to its substrate and absorb water and mineral salts. stem Main part of the moss from which the leaves spiral outward; it can be upright or flat. leaf Part of the moss originating at the stem, especially adapted to capture light, perform photosynthesis and absorb water. photosynthesis leaf margin
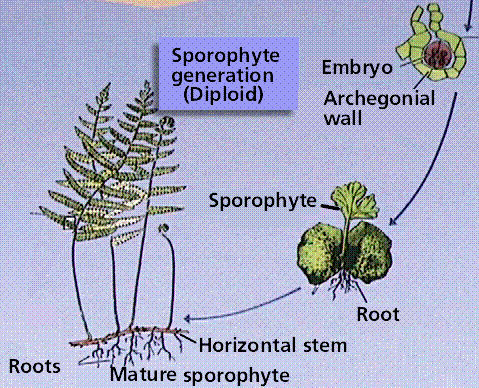
Draw a diagram to describe the life cycle of the moss, pointing out ... Solution. The life cycle of most mosses begins with the release of spores from a capsule, which opens when a small, lidlike structure, called the operculum, degenerates. A single spore germinates to form a branched, filamentous protonema, from which a leafy gametophyte develops. The gametophyte bears organs for sexual reproduction.
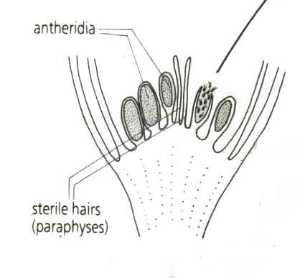
Moss Antheridia - Florida State University Moss Antheridia Reproduction of mosses, an advanced group of the green seedless plants known as Bryophytes, may take many forms. New plants may develop through branching, fragmentation, regeneration, or production of spores. In the gametophyte form of mosses, reproduction is generally sexual and is seasonally controlled.
Life cycle of a moss - Mosses - Te Ara Encyclopedia of New Zealand Life cycle of a moss. The familiar leafy moss plant is the sexual phase of the moss life cycle. When mature, most mosses develop sex organs . Some mosses have separate male and female plants, whereas others have male and female sex organs on the same plant. In wet conditions, sperm cells are released from male sex organs (antheridia) and swim ...
Fern Diagram Labeled Labeled Moss with Sporophytes In wet weather, sperm are released from . ( Marchantia) life cycle diagram; prepared slide of liverwort gemmae. Fern, any of several nonflowering vascular plants that possess true roots, stems, and complex leaves and that reproduce by spores. The number of known extant. Another way to tell if a plant is a fern is ...
30+ Different Types of Moss (And Most Common Moss Species) Springy Turf Moss . Scientific name: Rhytidiadelphus squarrosus Type: Acrocarpous Color: Pale green leaves and a red stem. Distribution: Widespread through temperate Northern Hemisphere, and introduced to the Southern Hemisphere. Characteristics: Commonly found in grass and lawns. It forms a spindly mat of branching stems that can extend up to 15 cm (6 inches) tall.
Mosses: Plant Body and Reproduction| Botany - Biology Discussion Moss plant reproduces by two methods, sexual and asexual. Plant itself bears the sexual units, sperms and egg. This part is called gamete-bearing part of gametophyte. When the two gametes fuse, zygote is formed, which develops into the sporogonium. Sporogonium in its turn bears asexual spores. That part is spore-bearing generation or sporophyte.
Primitive Plants: Mosses, Ferns, and Allies - biologyclermont.info Moss Archegonia with Eggs Examine (and draw and label) prepared slides of moss male antheridial heads and female archegonial heads. Labeled Moss with Sporophytes In wet weather, sperm are released from their antheridium, swim to an archegonium, swim down the opening in the archegonium, and fertilize the egg.
The Moss Life Cycle | Moss Gametophyte, Reproduction Parts & Diagram ... Moss life cycle diagram: the red boxes show the male antherdial part while the blue boxes show the female archegonial part, both are required for sexual reproduction. Both of the mature...
PDF Morphology of Mosses (Phylum Bryophyta) - eFloras.org The fundamental moss leaf consists of a unistratose lamina and a multistratose costa or midrib (Fig. 3). However, in a few families, the entire leaf is multistratose, and in many others, leaf margins are multistratose, or otherwise differentiated from the rest of the lamina (Fig. 4).
moss | Definition, Characteristics, Species, Types, & Facts Many small plants bearing the name moss are not in fact mosses. The "moss" found on the north side of trees is often the green alga Pleurococcus. Irish moss ( Chondrus crispus) is a red alga. Beard moss ( Usnea species), Iceland moss ( Cetraria islandica ), oak moss ( Evernia prunastri ), and reindeer moss ( Cladonia species) are lichens.
![Life cycle of moss [81] | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Serhat-Ursavas/publication/268502605/figure/fig4/AS:310560966103053@1451054912988/Life-cycle-of-moss-81.png)























Post a Comment for "43 moss plant labelled diagram"