40 cell membrane
Membrane | Definition, Structure, & Functions | Britannica Biological membranes have three primary functions: (1) they keep toxic substances out of the cell; (2) they contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules, such as ions, nutrients, wastes, and metabolic products, that mediate cellular and extracellular activities to pass between organelles and between the cell and the outside … Cell Membrane: Characteristics, Features, Functions And Structure The cell membrane or plasma membrane (or cytoplasmic) is the one that surrounds the cell . It serves as a barrier that mediates between the cell and the environment that surrounds it. It represents the boundary between the intracellular environment and the extracellular environment. It also works as a container for cell organelles.
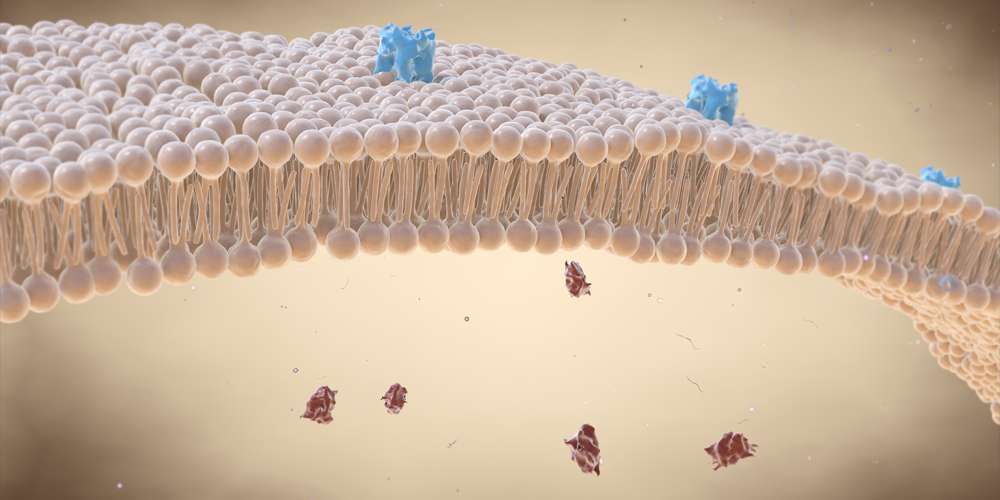
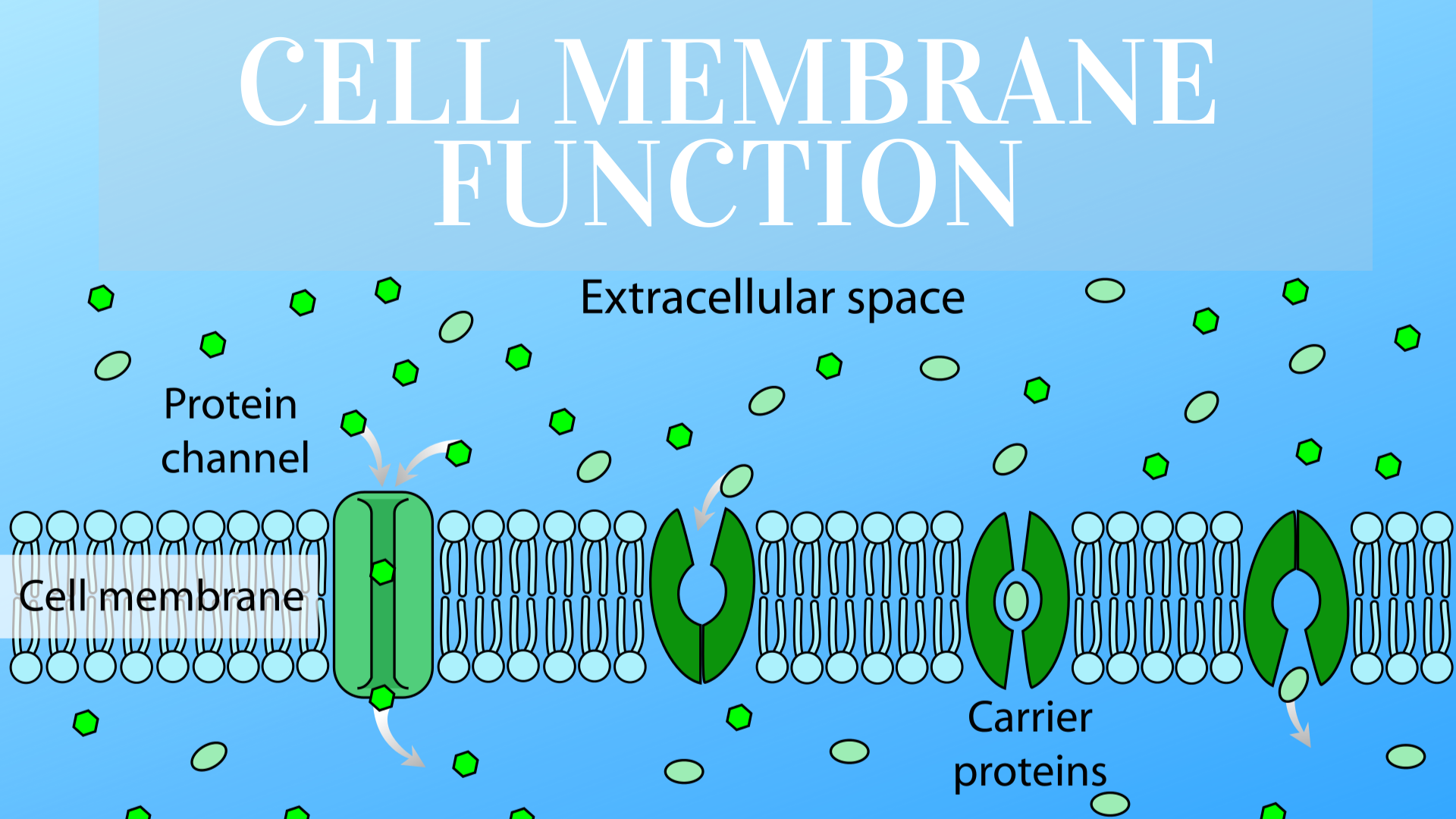
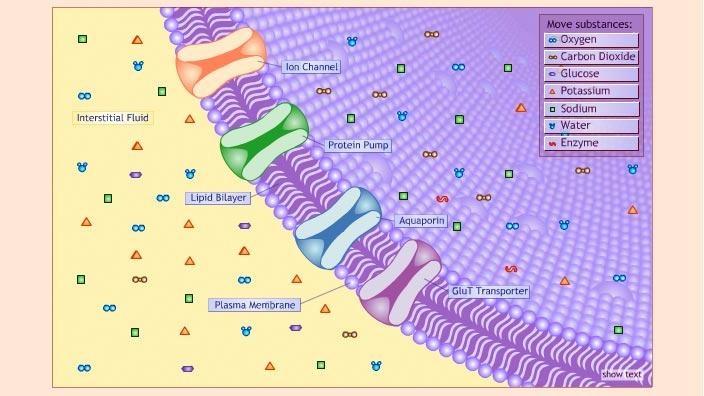
Cell membrane - Wikipedia The cell employs a number of transport mechanisms that involve biological membranes: 1. Passive osmosis and diffusion: Some substances (small molecules, ions) such as carbon dioxide (CO 2) and oxygen (O 2... 2. Transmembrane protein channels and transporters: Transmembrane proteins extend through ...
Cell membrane
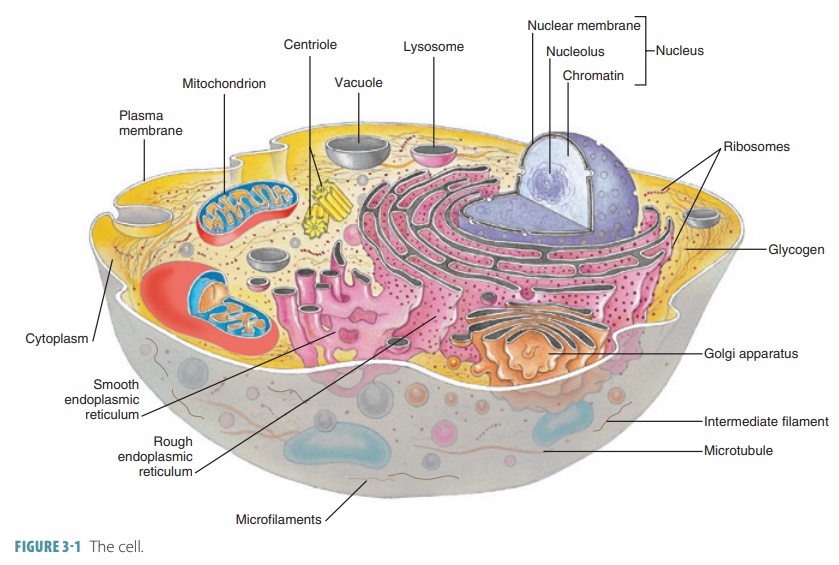
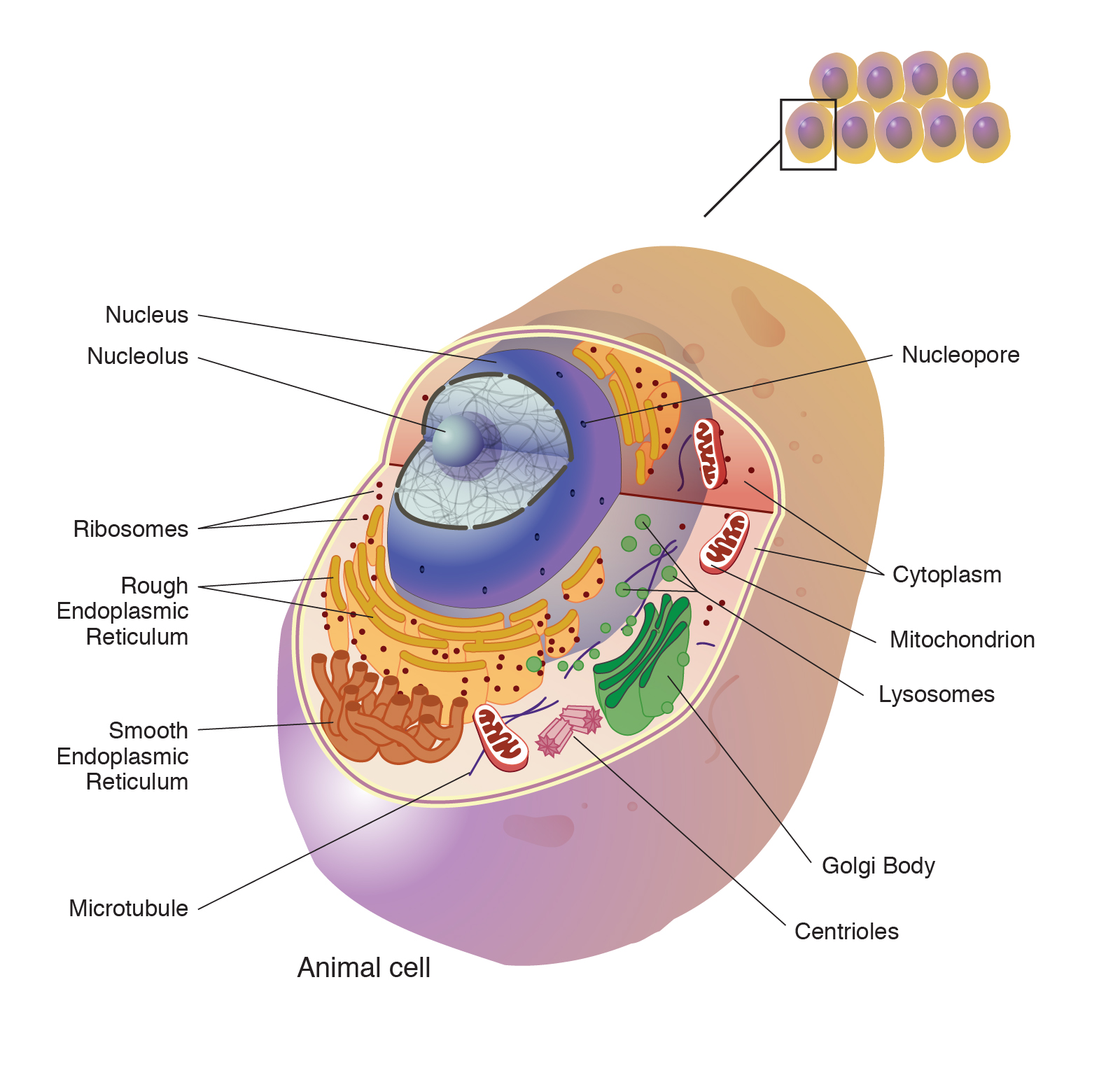
Membrane Structure - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Cell membranes are crucial to the life of the cell. The plasma membrane encloses the cell, defines its boundaries, and maintains the essential differences between the cytosol and the extracellular environment. Inside eucaryotic cells, the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other membrane-enclosed organelles maintain the characteristic differences between ... Cell Wall and Cell Membrane- Structure, Functions and Differences - BYJU'S The cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane. It provides protection for the cell and its cellular components from the external environment. It is selectively permeable and regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. 5. What is the primary component of the cell wall? Cell Membrane: Function And Definition - Science Trends The cell membrane also serves as an anchor point for the cytoskeleton of the cell in some organisms, and it attaches to the cell wall in plant cells. The cell membrane also helps regulate the growth of the cell, by controlling the processes of exocytosis and endocytosis.
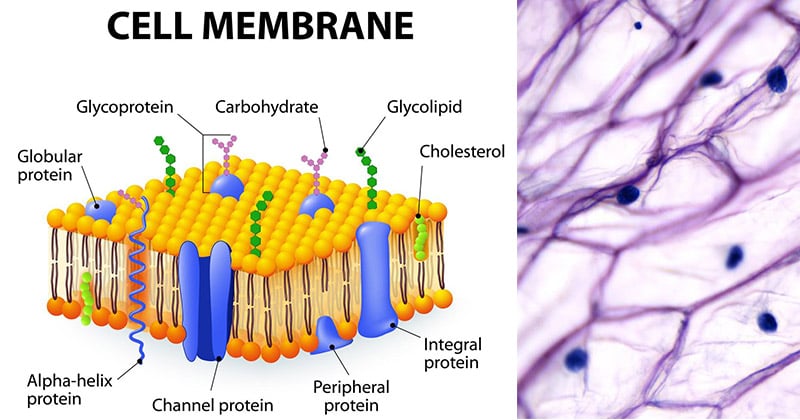
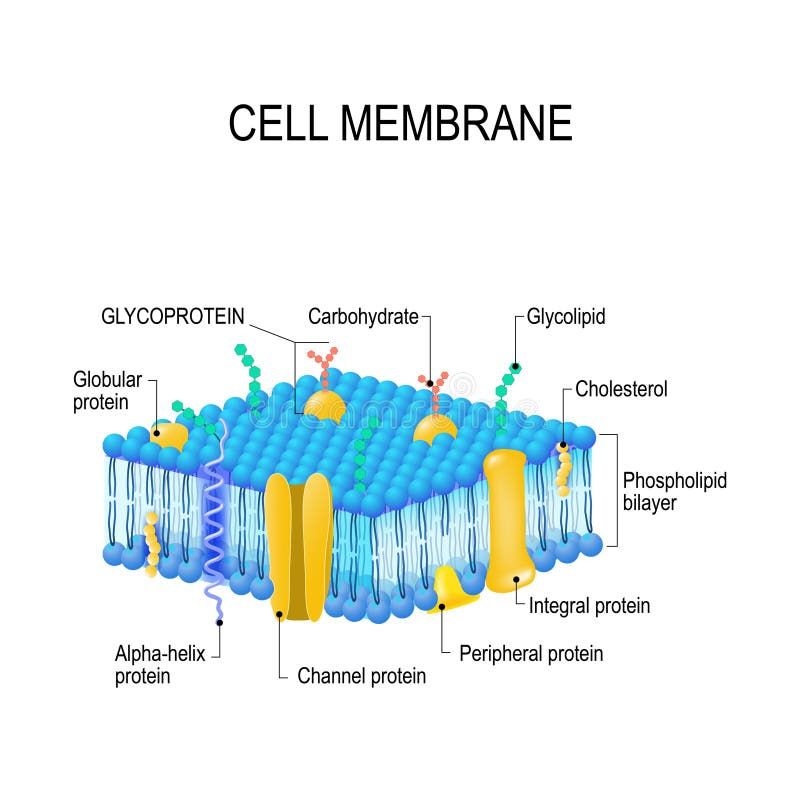
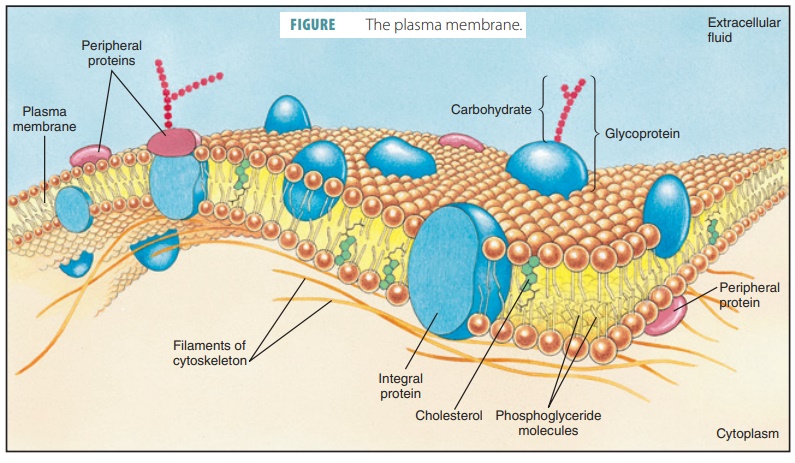
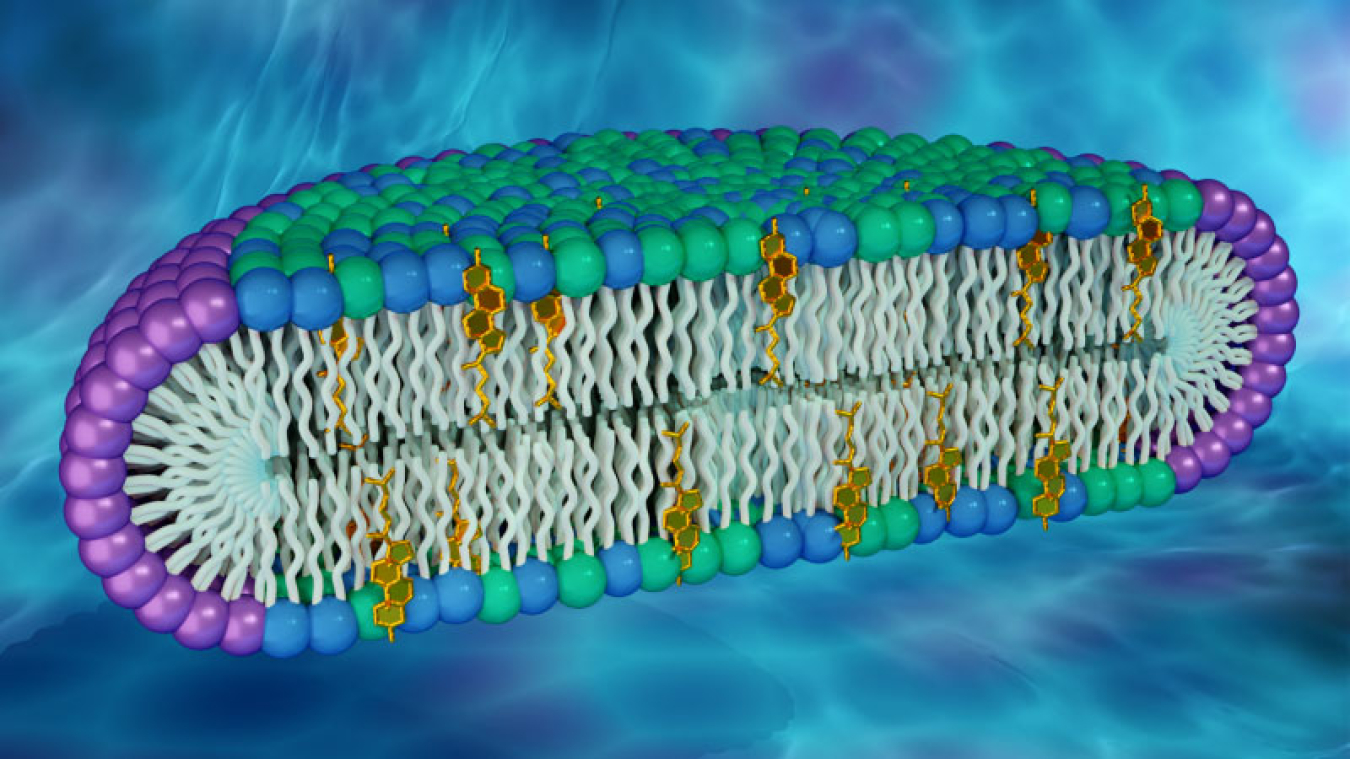
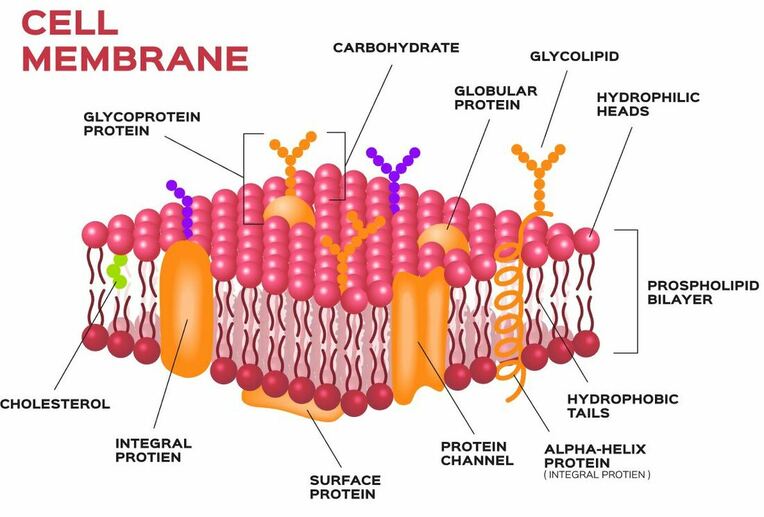
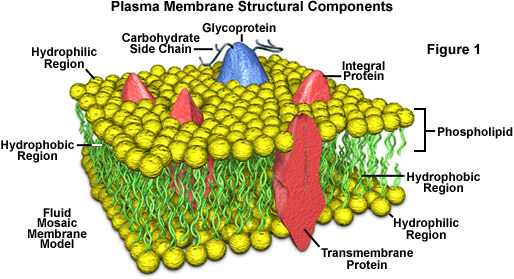
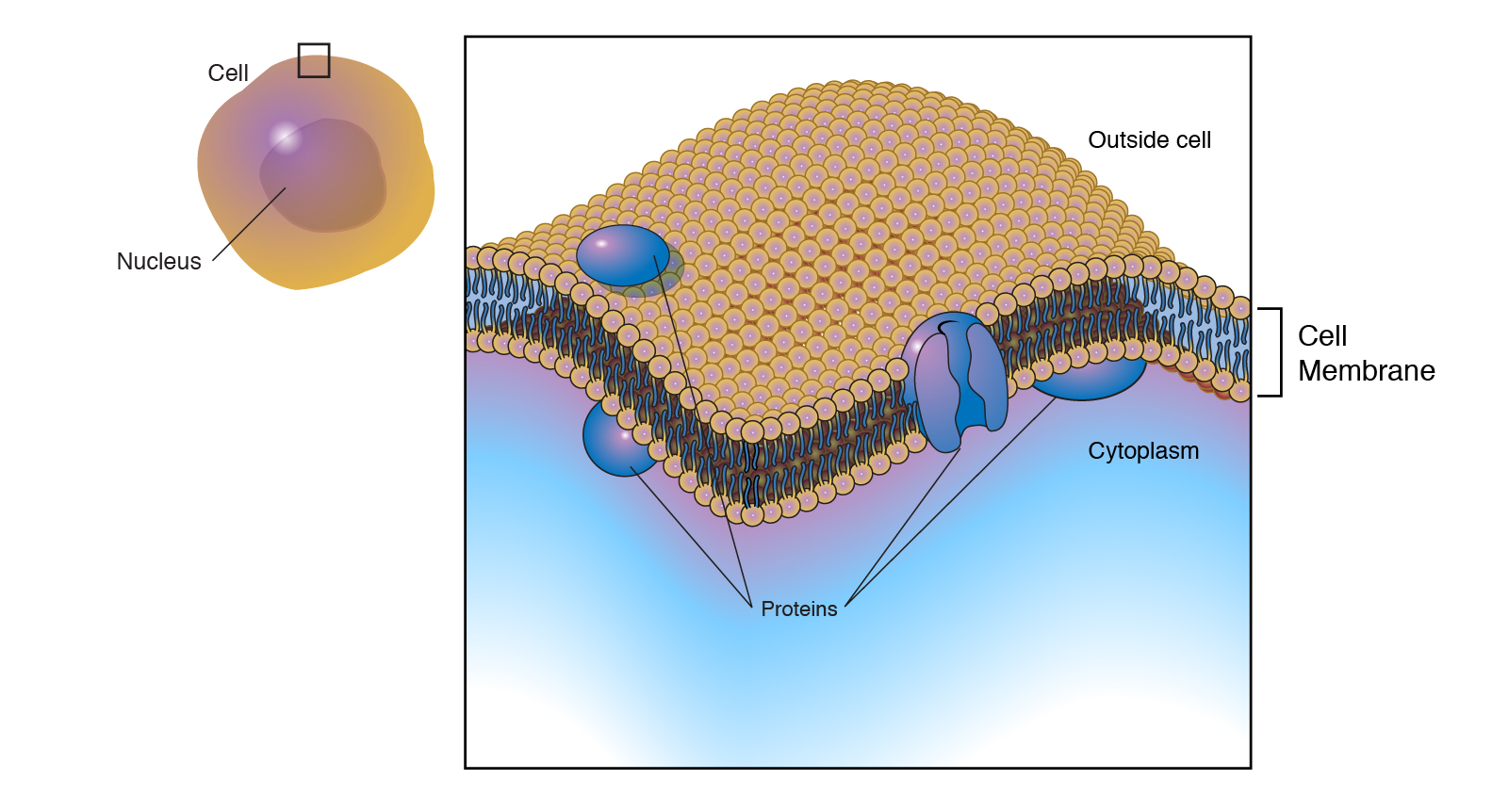
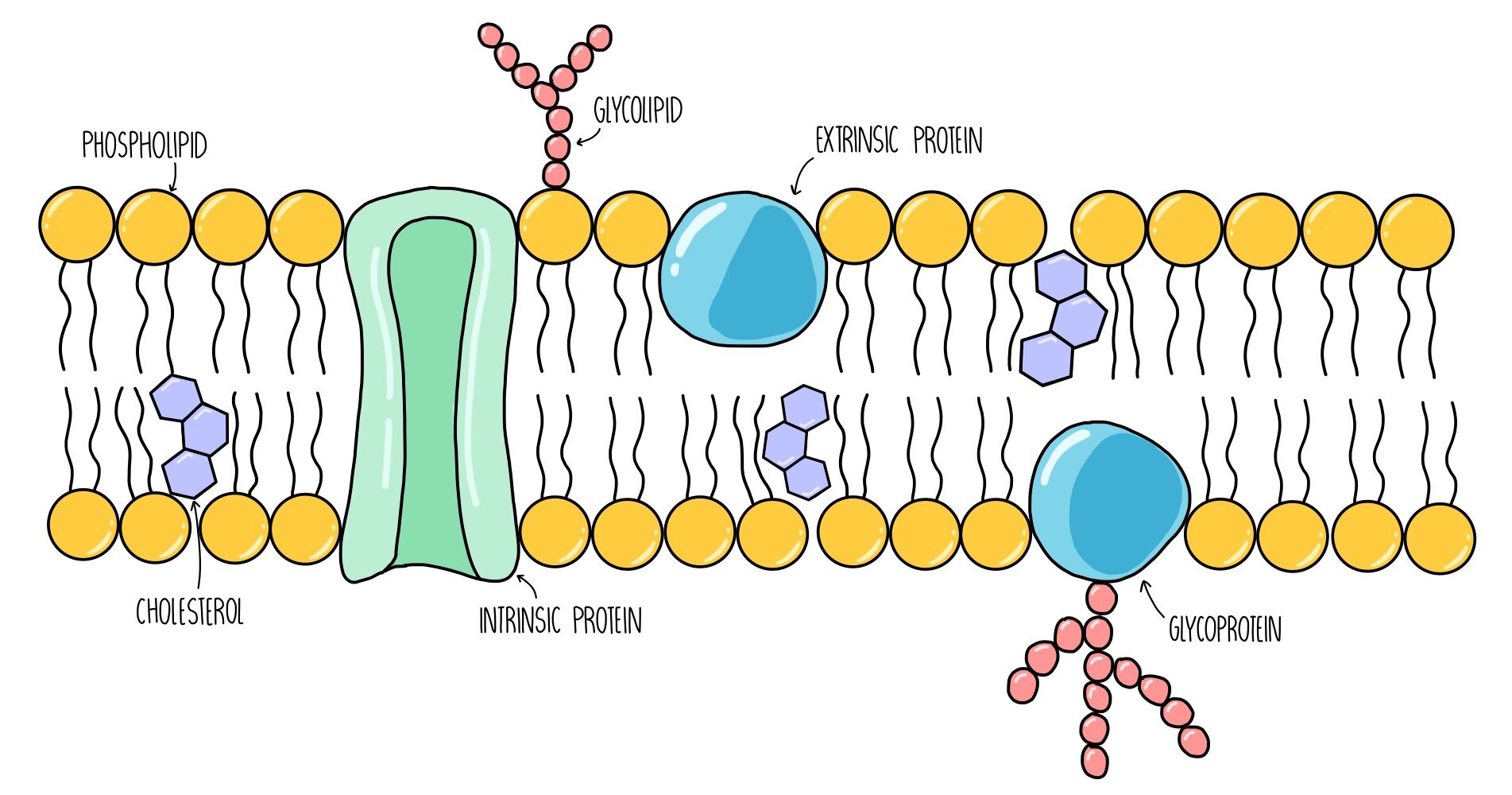
Cell membrane. 3.1 The Cell Membrane - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStax The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of back-to-back phospholipids (a "bilayer"). Cholesterol is also present, which contributes to the fluidity of the membrane, and there are various proteins embedded within the membrane that have a variety of functions. Cell Membranes | Learn Science at Scitable - Nature Cell membranes protect and organize cells. All cells have an outer plasma membrane that regulates not only what enters the cell, but also how much of any given substance comes in. Unlike... 3.4: The Cell Membrane - Biology LibreTexts 1) Figure 3.4. 1: The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane structure describes the plasma membrane as a fluid combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. The plasma membrane is made up primarily of a bilayer of phospholipids with embedded proteins, carbohydrates, glycolipids, and glycoproteins, and, in animal ... The cell membrane - Transport across membranes - BBC Bitesize The cell membrane is selectively permeable. It lets some substances pass through rapidly and some substances pass through more slowly, but prevents other substances passing through it at all....
Cell Membrane - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. It separates the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell) from the external environment. It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. a 3D diagram of the cell membrane Function of the Cell Membrane 3.1 The Cell Membrane – Anatomy & Physiology The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two layers of phospholipids (a “bilayer”). Cholesterol and various proteins are also embedded within the membrane giving the membrane a variety of functions described below. Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane) - Genome.gov The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell. Narration 00:00 … Cell membrane - definition, structure, function, and biology The cell membrane is a thin biological membrane that separates the interior of cells from the outside space and protects the cells from the surrounding environment. The cell membrane is made of two layers of lipid films (oil molecules) with many kinds of proteins inserted.
The Cell Membrane | Biology I - Lumen Learning A cell's plasma membrane defines the boundary of the cell and determines the nature of its contact with the environment. Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others, all in controlled quantities. Plasma membranes enclose the borders of cells, but rather than being a static bag, they are dynamic and constantly in ... Cell membrane | Osmosis The cell membrane is an important structural element of the building block of life - the cell. Its main role is to define what's inside - the intracellular space - and what's outside - the extracellular space. It also regulates what comes in or out of the cell - that's called selective permeability. Cell Membrane Structure and Function - Biology Wise Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell (in animals). In plant cells, the membrane encapsulates the protoplasm. This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane. Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes. Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) - Genome.gov Definition. The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable.
Cell Membrane: Definition, Structure, & Functions with Diagram Cell Membrane: Structure, Composition, and Functions The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is a thin layer that surrounds the cytoplasm of all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including plant and animal cells.
Inside the Cell Membrane - YouTube Explore the parts of the cell membrane with The Amoeba Sisters! Video discusses phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol, peripheral proteins, integral proteins, glycoproteins, and glycolipids - as well...
Cell Membrane Function & Importance | What is a Cell Membrane ... A cell membrane is a semipermeable outer covering of cells. Cells in animals, plants, fungi, and prokaryotes have cell membranes. The cell membrane is made primarily of lipids and proteins and is ...
What Does the Cell Membrane Do in a Plant Cell? - Study.com The cell membrane is the semi-permeable structure that surrounds the cell. Something that is semi-permeable will allow specific substances to pass through it while preventing the passage of other ...
Cell Membrane Function and Structure - ThoughtCo Oct 7, 2019 · Key Takeaways The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cell's cytoplasm. It protects the integrity of the cell... Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane. The exact mix or ratio of proteins and lipids can... Phospholipids are important components of ...
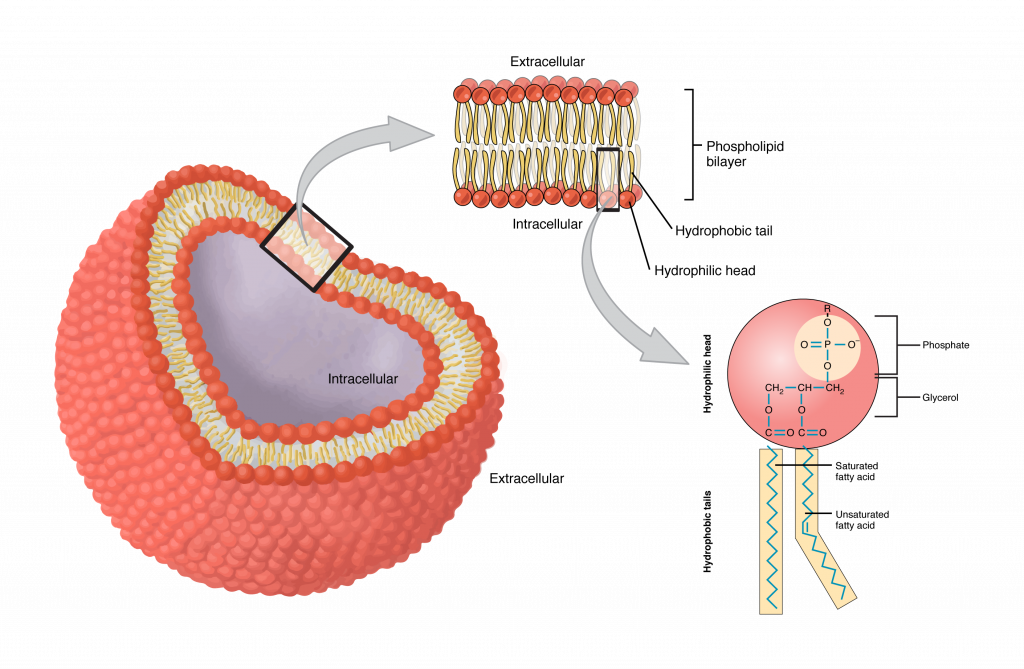
Structure of the plasma membrane (article) | Khan Academy The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group.
Cell membrane | Definition, Function, & Structure | Britannica The cell membrane, therefore, has two functions: first, to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and, second, to be a gate allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products. Cell membranes are composed primarily of fatty-acid-based lipids and proteins.
The cell membrane review (article) | Khan Academy The cell membrane contains a phospholipid bilayer, but the terms are not interchangeable. Part of the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer, made of two layers of phospholipid molecules. However, the cell membrane also contains other macromolecules like membrane proteins, and carbohydrates.
Cell Membrane: Definition, Structure, and Examples - Research Tweet Cells are the structural, functional, and biological units that make up all living things. It's a membrane-bound cytoplasmic structure with cytoplasmic structures. The cell membrane is the membrane that surrounds the cell and isolates it from the outside world. The plasma membrane is the cell's outermost layer in mammals, although it is ...
Cell Membrane: Function And Definition - Science Trends The cell membrane also serves as an anchor point for the cytoskeleton of the cell in some organisms, and it attaches to the cell wall in plant cells. The cell membrane also helps regulate the growth of the cell, by controlling the processes of exocytosis and endocytosis.
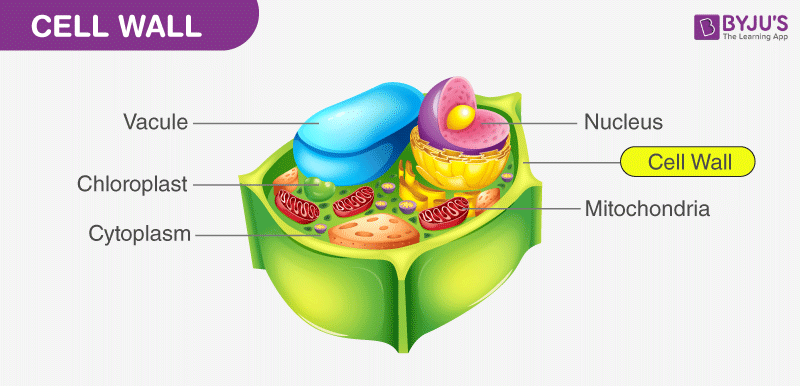
Cell Wall and Cell Membrane- Structure, Functions and Differences - BYJU'S The cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane. It provides protection for the cell and its cellular components from the external environment. It is selectively permeable and regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. 5. What is the primary component of the cell wall?
Membrane Structure - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Cell membranes are crucial to the life of the cell. The plasma membrane encloses the cell, defines its boundaries, and maintains the essential differences between the cytosol and the extracellular environment. Inside eucaryotic cells, the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other membrane-enclosed organelles maintain the characteristic differences between ...





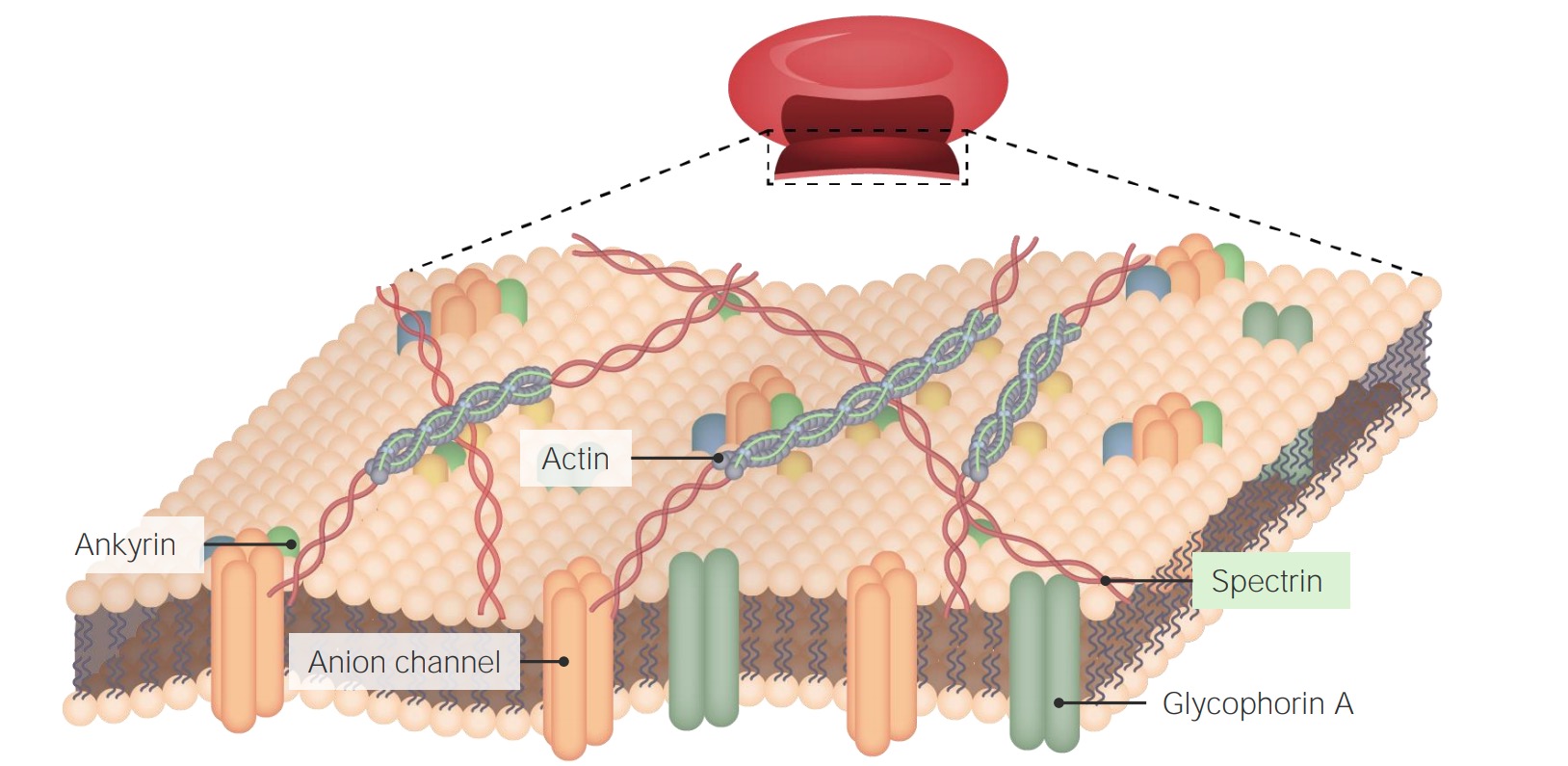



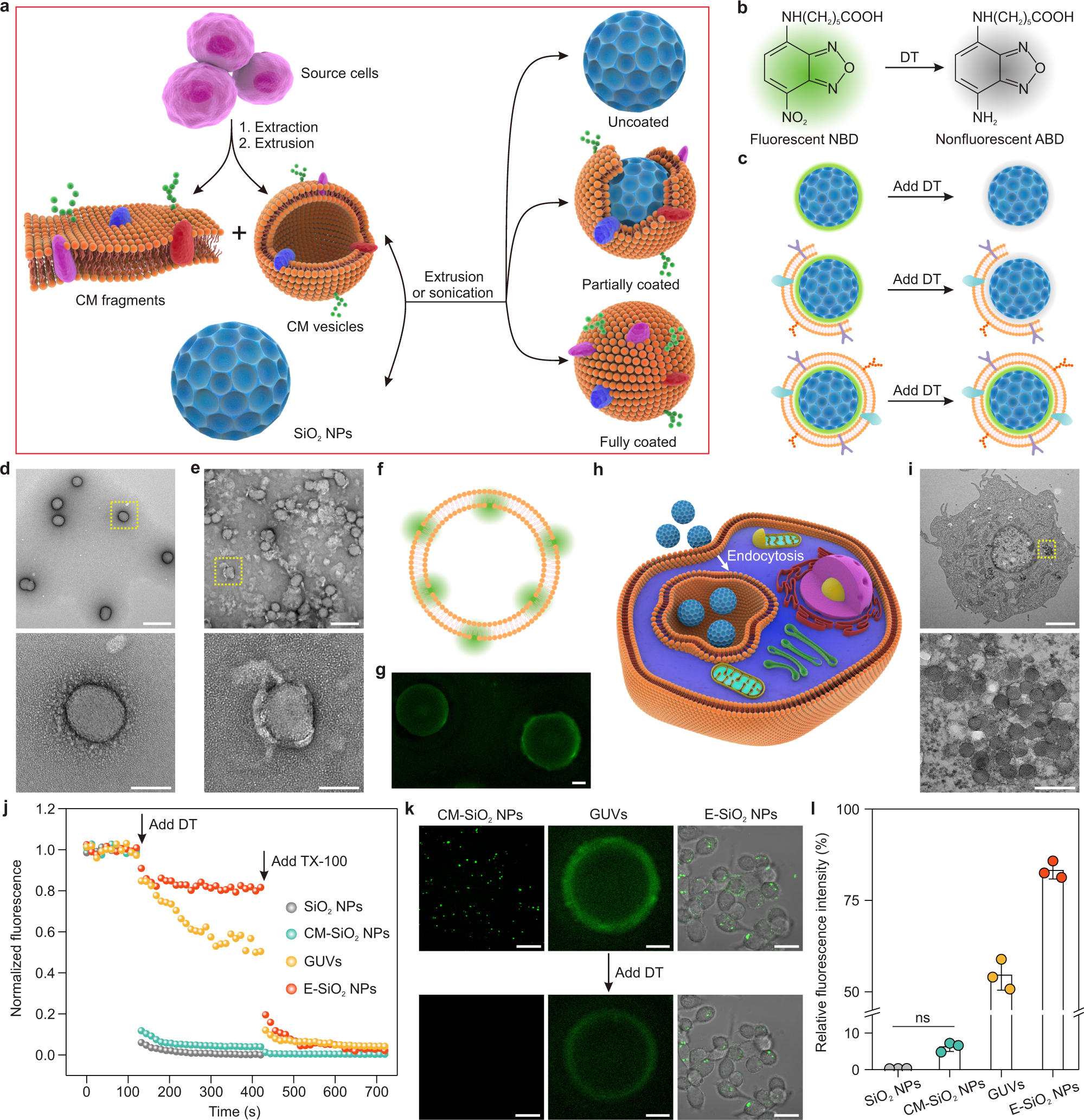
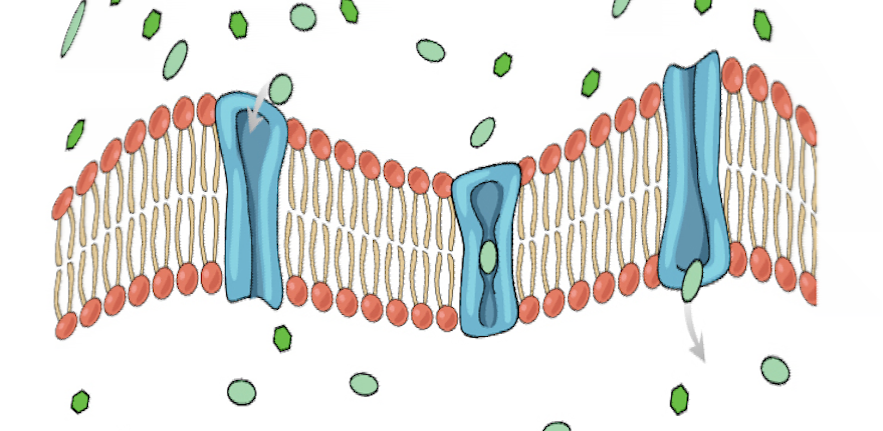
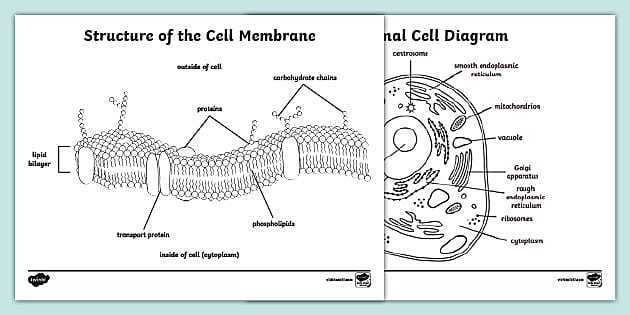

:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14571/Cell_Membrane_V2-.png)






Post a Comment for "40 cell membrane"